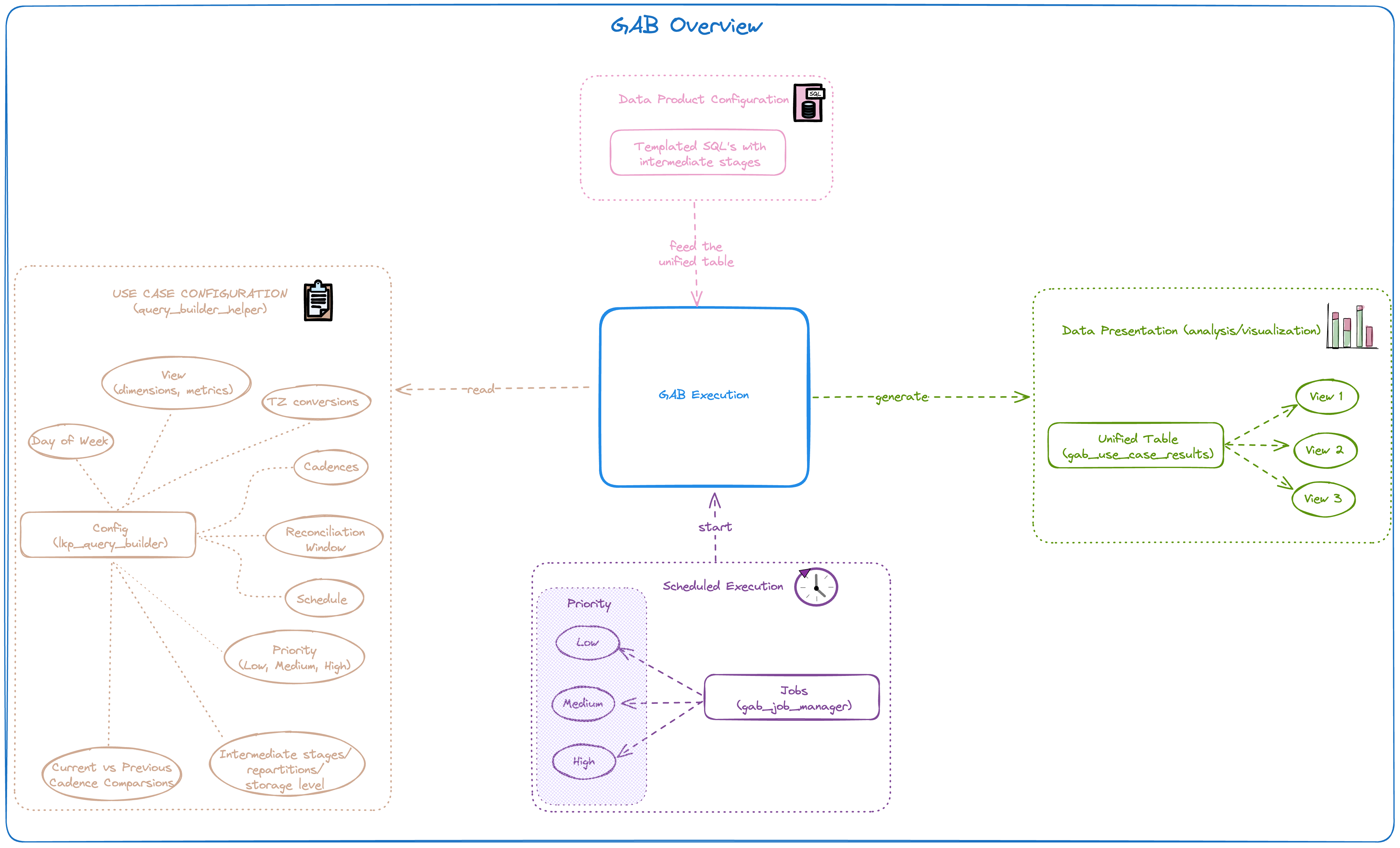
GAB - Gold Asset Builder
GAB stands for Gold Asset Builder and, technically, it is a SQL-first transformation workflow that allows teams to, quickly and collaboratively, deploy aggregate tables on top of base fact tables, which can then be used for empowering analytics over different perspectives on dashboards or exploratory queries.
Main benefits:
- Efficiency and speed: It reduces the efforts and time to production for new aggregate tables (gold layer assets).
- Simple pipeline: It simplifies the cluster decision by having just 3 cluster types (small, medium, large), there's no need to create a separated pipeline for each case.
- Low-code and mainly SQL language.
Before deciding whether your use case will fit into GAB or not, please read the instructions in the sections below carefully. If there is any doubt about certain metrics which might deviate from our framework support please reach us before starting your development. GAB may not be a one size fit for all your requirements so please make use of the framework only if it satisfies your criteria.
Advantages
- More flexibility to define any type of complex sql queries.
- Only need to touch the sql file for the execution
- Quick production rollout and adaptability
- Innersourcing model really works, a data analyst can work on sql and hand it over to the engineering team. Engineering team can then adapt the templating and make the production ready code quickly after the data validation.
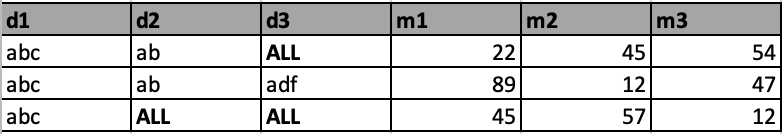
- As shown in the image below, it's possible to generate different perspectives of the same metric for a specific use case:
- rollup (aggregated by dimension1(d1), dimension2(d2)) - Compute the same metrics at a upper level from the most granular level
- grouping set (aggregated by dimension1(d1), dimension2(d2), dimension3(d3)) - Compute the same metrics at the most granular level
- cube (aggregated by dimension1(d1)) - Compute the same metrics in the higher aggregation level
Use GAB
- When an aggregate table is to be created for any analytical perspectives on dashboards or exploratory queries with some specific dimensions and metrics and can be done using normal SQL query.
- When metrics and dimensions are bound to the configured cadences and you are not calculating the whole universe data in your SQL query.
Don't Use GAB
- When metrics and dimensions are not bound to cadences.
- When your table is not an aggregated i.e. table is at an acid granularity
- When your metrics are not calculated incrementally.
GAB Capabilities
Cadence
In which cadence (timeslice) you want the data (DAILY, WEEKLY, MONTHLY, QUARTERLY, YEARLY).
Dimensions/Metrics
Dimension
Usually directly mapped from the table without any transformation, it will be used to aggregate the metric, example: product_category.
Metric
Aggregated value at the dimension level with the cadence as one of the dimension. There's some options to compute a metric:
- Directly from a table column, example:
sum(product_amount) - Compute it in the same cadence but in an exactly 1 previous time window, example: In a
MONTHLYcadence it will compute for the previous month. - Compute it in the same cadence but from the last year, example: In a
QUARTERLYcadence it will compute it in the same quarter but from the previous year. - Compute it in the same cadence but with a custom window function, example: In a
QUARTERcadence computing the last 2 quarters. - Compute it in any SQL way possible: using any of the available columns, deriving a metric from another, using SQL functions, etc. Example: compute a metric for the last 6 months of data.
Note: each computation derives a new column on the output view.
Extended Window Calculator & Reconciliation
Extended window Calculator
This feature aims to calculate the extended window of any cadence despite the user providing custom dates which are not the exact start and end dates of a cadence.
- For example, if the user wants to calculate the
MONTHcadence but gives a date range of2023-01-10to2023-01-29, the computation window will be a window from2023-01-01to2023-01-31, which calculates the full data for the month and inserts it. This function handles any user error to efficiently integrate the data.
{'DAY':{},'WEEK':{},'MONTH':{},'YEAR':{}}
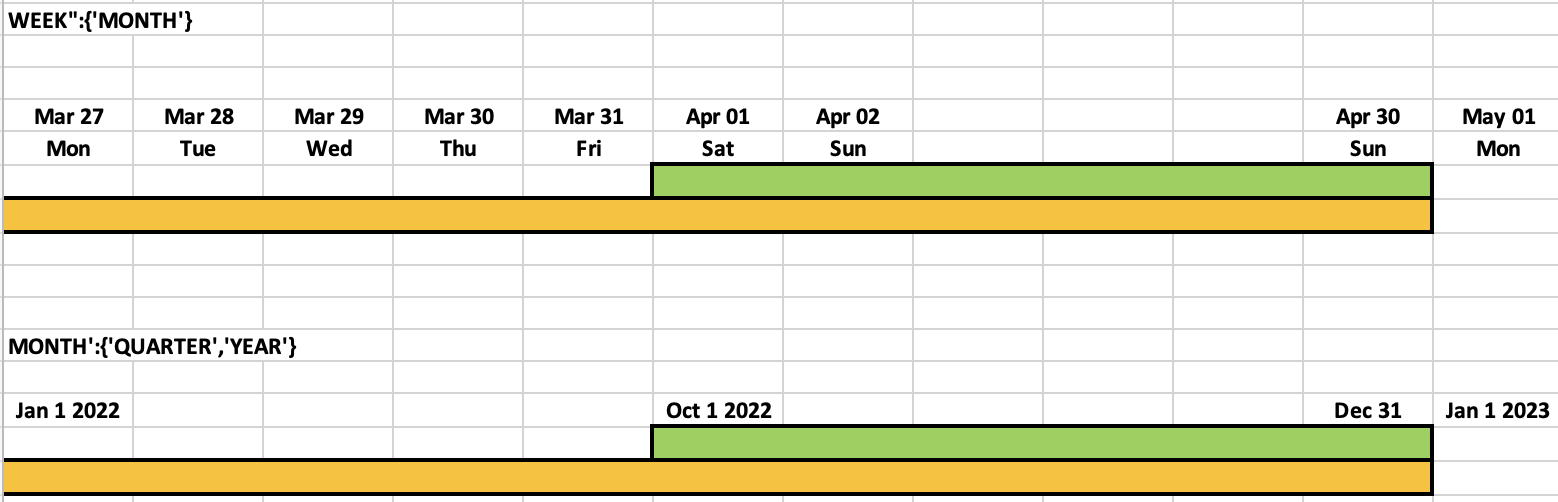
You can find an image below sampling how a recon_window config looks like. If we consider WEEK cadence, then it has a recon_window of MONTH and QUARTER. What this means is, at the start of a new Month or a Quarter, all the weeks in that cadence are recalculated to consider the late events. For example, 2023-01-01 is the start of a Month, Quarter and a Year. Here since Month and Quarter are given and Quarter is the greater cadence among the 2, all the weeks in Q4 2022 (with the extended cadence window using the above function) are recalculated i.e. instead of 2022-10-01 to 2022-12-31, extended window is 2022-09-26 to 2023-01-01.
Reconciliation
Reconciliation enables the user to compute the data aggregated by the specified cadence but in a different frequency, this brings flexibility in the data computation as the use case can compute the data in a smaller or bigger frequency, example:
- There's a use case where the cadence is
WEEKLYbut we want the aggregated data with aDAILYfrequency, so configuring the reconciliation window to beDAILYit will compute the data inWEEK TO DATEbasis (In a case where the first day of week is monday, on monday it will have the data just for monday, on tuesday will be the computation of monday + tuesday, on wednesday will be the computation of monday + tuesday + wednesday, and so on until the end of week), configuration example:
{'WEEK': {'recon_window': {'DAY': {'snapshot': 'N'}}}}
- You can also have the same frequency calculation but with in a bigger frequency, like
WEEKLYcadence but compute it just with aMONTHLYfrequency, configuration example:
{'WEEK': {'recon_window': {'MONTH': {'snapshot': 'N'}}}}
Snapshot
It creates a snapshot of the computed data on the specified reconciliation cadence, example: in a case where we have MONTHLY cadence and snapshot enabled at DAILY basis, we are going to compute the use case for each day in the month. Use case configuration:
{'MONTH': {'recon_window': {'DAY': {'snapshot': 'Y'}}}}
Next Steps
If you are interested in using GAB you can check our step-by-step documentation that aims to help in the use case configuration and make easier to use this awesome feature :)